Our picks for LLC formation services
 |
Most recommended Tailor Brands |
|
Visit Tailor Brands |
 |
Northwest Registered Agent |
|
Visit Northwest |
 |
ZenBusiness |
|
Visit ZenBusiness |
 |
LegalZoom |
|
Visit LegalZoom |
FAQs
What is the process for registering an LLC in Utah?
The process of forming an LLC in Utah involves several steps, including choosing a unique name for your business, filing the Utah Certificate of Organization, appointing a registered agent, and drafting an operating agreement if desired. Once these requirements are fulfilled and the necessary fees are paid, your LLC will be officially registered with the state.
Do I need to have a physical address in Utah to form an LLC?
Yes, you’ll need to obtain a physical address for your Utah LLC’s registered agent, which cannot be a P.O. Box. However, you can use a P.O. Box as your business address for mailing purposes if desired.
Are there any restrictions on the types of businesses that can form an LLC in Utah?
In Utah, there are generally no restrictions on the types of businesses that can form an LLC, including sole proprietorships looking to transition to a more formal business structure. LLCs offer liability protection and other benefits that can be advantageous for sole proprietors seeking to separate their personal and business affairs.
What is the process for dissolving an LLC in Utah?
To dissolve an LLC in Utah, you must file Articles of Dissolution with the Utah Division of Corporations and Commercial Code. This document formally terminates the existence of your LLC and should be accompanied by any required fees and paperwork. Once approved, your Utah LLC will no longer be considered active, and you’ll need to fulfill any remaining obligations before officially closing the business.
Can I trademark my LLC's name in Utah?
Yes, you can trademark your LLC’s name in Utah to protect its identity and brand. To trademark your LLC’s name in Utah, you would need to file a trademark application with the Utah Department of Commerce, Division of Corporations and Commercial Code, or seek federal trademark registration through the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO).
When starting a new company, choosing a business entity is the most important decision that the founders must make. For most businesses with more than one founding member, forming an LLC is often the best option for a number of reasons.
An LLC is an uncomplicated business structure that affords business owners legal protection by separating personal assets from business debts. Moreover, LLCs often enjoy a lower tax rate than corporations. Nevertheless, creating an LLC can get complicated depending on where you are based, with the formation process, filing fees, and continuing legal obligations differing from state to state.
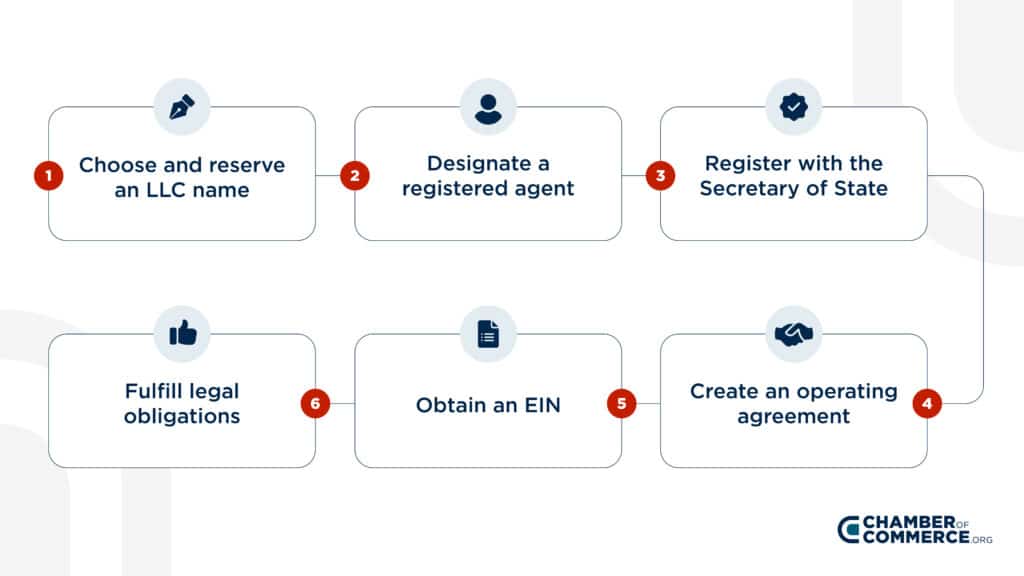
Starting an LLC in Utah step-by-step
1. Select a name for your Utah LLC
Follow naming requirements
There are two major guidelines to follow when naming your LLC in the State of Utah:
- An LLC’s name must be distinguishable from the names of existing business entities on file with the Utah Division of Corporations and Commercial Code.
- An LLC’s name must contain
Need help coming up with a business name? Check out our free business name generator.
Check name availability
Confirm that your chosen LLC name is available in Utah using the Division of Corporations and Commercial Code Business Search.
Reserve your LLC name with the Division of Corporations
Reserving your LLC name with the Division of Corporations is a good idea because it prevents another business from using it before you can legally organize your business in Utah.
File an Application for Reservation of Business Name with the Utah Division of Corporations online or by postal mail to reserve your name for up to 120 days. The filing fee is $22.
2. Designate a registered agent
As in every U.S. state, forming an LLC in Utah requires the appointment of a registered agent service to handle state and federal legal documents and service of process on the business’s behalf.
The registered agent must either be a state resident or business entity with a street address in Utah OR if the individual or business is based out-of-state, they must have a business office in Utah.
Our picks of the best registered agent services
- Northwest Registered Agent: Starting a business requires a lot of state-mandated paperwork, which can be confusing for new business owners. Northwest offers business services that can help entrepreneurs find the right documentation, fill it out, and file it on time with the right government agency. In addition to helping you set up an LLC, Northwest has a host of additional services, like registered agent services, that new owners will find useful too.
- ZenBusiness: There’s no need to stress about filing paperwork when you work with ZenBusiness. This company offers a great variety of LLC services, the focus of which is to ensure your business is set up correctly with the proper paperwork filled out and delivered to the right branch of your state government. Of course, ZenBusiness does charge for their services, but customers say they get the most bang for their buck.
- Harbor Compliance is a great fit for organizations that register in multiple states and for those who don’t want to pay excessive service fees. With their network and electronic document delivery, they help ensure your business never misses a legal notification.
FAQs
What is the process for registering an LLC in Utah?
The process of forming an LLC in Utah involves several steps, including choosing a unique name for your business, filing the Utah Certificate of Organization, appointing a registered agent, and drafting an operating agreement if desired. Once these requirements are fulfilled and the necessary fees are paid, your LLC will be officially registered with the state.
Do I need to have a physical address in Utah to form an LLC?
Yes, you’ll need to obtain a physical address for your Utah LLC’s registered agent, which cannot be a P.O. Box. However, you can use a P.O. Box as your business address for mailing purposes if desired.
Are there any restrictions on the types of businesses that can form an LLC in Utah?
In Utah, there are generally no restrictions on the types of businesses that can form an LLC, including sole proprietorships looking to transition to a more formal business structure. LLCs offer liability protection and other benefits that can be advantageous for sole proprietors seeking to separate their personal and business affairs.
What is the process for dissolving an LLC in Utah?
To dissolve an LLC in Utah, you must file Articles of Dissolution with the Utah Division of Corporations and Commercial Code. This document formally terminates the existence of your LLC and should be accompanied by any required fees and paperwork. Once approved, your Utah LLC will no longer be considered active, and you’ll need to fulfill any remaining obligations before officially closing the business.
Can I trademark my LLC's name in Utah?
Yes, you can trademark your LLC’s name in Utah to protect its identity and brand. To trademark your LLC’s name in Utah, you would need to file a trademark application with the Utah Department of Commerce, Division of Corporations and Commercial Code, or seek federal trademark registration through the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO).
3. File a Certificate of Organization
An LLC is formed in Utah through the filing of a Certificate of Organization with the Utah Division of Corporations.
The Certificate of Organization must provide the following information:
- LLC’s name and the address of its principal office
- Registered agent name and address
- LLC members’ names and addresses (optional)
- The signature of an LLC organizer
You can file the certificate online using the Utah Online Business Registration website or by postal mail. The filing fee is $59.
4. Create an operating agreement
Although not a legally mandated step for forming an LLC in Utah, drafting a comprehensive LLC operating agreement is strongly recommended for all nascent companies, whether LLCs or corporations.
The operating agreement should do the following:
- Describe the LLC’s business structure
- Establish the individual responsibilities and obligations of LLC members
- Detail how the LLC will be run
Without an operating agreement clarifying the specific duties of its members, an LLC may face significant legal and operational difficulties.
5. Obtain an IRS Employer Identification Number (EIN)
All newly formed LLCs in the United States must acquire an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the Internal Revenue Service (with the exception of single-member LLCs). The nine-digit EIN is like a social security number for a business and is necessary to pay income tax, file tax returns, open business bank accounts, and perform many other important functions.
You can apply for an EIN online on the IRS website without paying a filing fee.
6. Fulfill your legal obligations
Once an LLC is registered, its members must devote attention to fulfilling legal requirements that apply for the duration of the company’s existence.
File Annual Renewals
All LLCs doing business in Utah (including foreign LLCs) are required to file an annual renewal (a.k.a. annual report) with the Utah Division of Corporations each year and pay a $18 filing fee. An LLC’s initial annual renewal is due by the one-year anniversary of its registration or authorization to do business in the state, and subsequent annual renewals are due each year on the same date.
File the annual renewal online or download a blank form, complete it, and mail it to the Division of Corporations.
Obtain business licenses and permits
For a Utah LLC operating statewide, certain licenses and permits are necessary to ensure compliance with state regulations. No general license is required for LLCs.
- Sales Tax Registration: If your business sells taxable goods or services, obtaining a Seller’s Permit is crucial. Fortunately, it’s a straightforward process facilitated through Utah’s One Stop Business Registration website, and the best part is that it’s free with no renewal required.
- Local licenses: In addition to statewide requirements, businesses operating within Utah must also consider local regulations. While the state itself doesn’t mandate a general business license, individual cities and counties may have their own stipulations. Call your local city or county clerk to inquire about local licenses and you can find a list of these offices in the Utah State Government’s Business Licensing & Registration Guide.
- Occupational licenses: Furthermore, certain professions or industries within Utah may have industry-specific licensing requirements. The state typically issues these licenses or permits, which are crucial for legal operation. Industries such as cosmetology, construction, healthcare, and food service often fall under this category. To ensure compliance with these specific regulations, it’s essential to consult the relevant state agency governing your industry.
Visit the Utah Division of Occupational and Professional Licensing site for information on additional occupational licenses and permits that may be required for your LLC, depending on its type of business.
Understand state taxes
Utah LLCs operate as pass-through entities, meaning the LLC itself doesn’t pay state income tax. Instead, profits and losses pass through to individual members who report them on their personal income tax returns.
Utah tax rate: Members are taxed at the flat rate of 4.85% on their share of the LLC’s profits as Utah State Income Tax.
Employer taxes: Employer taxes are another consideration for Utah LLCs with employees. LLCs must withhold state and federal income taxes from employee paychecks and contribute to state unemployment insurance taxes. These obligations require careful record-keeping and adherence to state and federal tax regulations to avoid legal consequences.
Additional tax considerations: Also, certain industries may face additional taxes or fees imposed by the state. These industry-specific taxes vary depending on the nature of the business and can include licensing fees, excise taxes, or special assessments. LLCs operating in such industries must research and understand the specific tax requirements applicable to their business activities to ensure compliance and avoid potential financial liabilities.
Register with the Utah State Tax Commission: LLCs active in Utah (including foreign LLCs) may be required to register with the State Tax Commission to pay a number of state taxes. This includes LLCs that collect sales tax on retail goods and LLCs that have employees. You can register with the Tax Commission online, or by completing a paper application and mailing it in.
Understand BOI reporting
Important Update (March 2025): FinCEN has removed Beneficial Ownership Information (BOI) reporting requirements for U.S.-formed companies. Domestic LLCs are no longer required to file BOI reports.
The recently enacted Beneficial Ownership Information (BOI) rules, established through the Corporate Transparency Act, seek to enhance transparency surrounding business ownership and combat financial crimes.
Who must file: Reporting entities encompass a variety of legal structures, including corporations, LLCs, and certain foreign entities registered in the US.
Deadlines to file: To facilitate this process, reports are electronically submitted through the Beneficial Ownership Secure System (BOSS), developed by FinCEN. Deadlines to file are as follows:
- For reporting deadlines, companies established before 2024 must submit their initial report by January 1, 2025.
- Those formed in 2024 are required to report within 90 days of receiving notice of their formation or registration.
- Entities formed in 2025 must report within 30 days of such notice.
- Any updates or modifications to the reported information must be promptly disclosed within 30 days.
Learn more about BOI Reporting.
LegalZoom can help you file a compliant and stress-free BOI Report for only $149.
FAQs
What is the process for registering an LLC in Utah?
The process of forming an LLC in Utah involves several steps, including choosing a unique name for your business, filing the Utah Certificate of Organization, appointing a registered agent, and drafting an operating agreement if desired. Once these requirements are fulfilled and the necessary fees are paid, your LLC will be officially registered with the state.
Do I need to have a physical address in Utah to form an LLC?
Yes, you’ll need to obtain a physical address for your Utah LLC’s registered agent, which cannot be a P.O. Box. However, you can use a P.O. Box as your business address for mailing purposes if desired.
Are there any restrictions on the types of businesses that can form an LLC in Utah?
In Utah, there are generally no restrictions on the types of businesses that can form an LLC, including sole proprietorships looking to transition to a more formal business structure. LLCs offer liability protection and other benefits that can be advantageous for sole proprietors seeking to separate their personal and business affairs.
What is the process for dissolving an LLC in Utah?
To dissolve an LLC in Utah, you must file Articles of Dissolution with the Utah Division of Corporations and Commercial Code. This document formally terminates the existence of your LLC and should be accompanied by any required fees and paperwork. Once approved, your Utah LLC will no longer be considered active, and you’ll need to fulfill any remaining obligations before officially closing the business.
Can I trademark my LLC's name in Utah?
Yes, you can trademark your LLC’s name in Utah to protect its identity and brand. To trademark your LLC’s name in Utah, you would need to file a trademark application with the Utah Department of Commerce, Division of Corporations and Commercial Code, or seek federal trademark registration through the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO).
Post LLC tasks
Set up business bank accounts
While not legally required, having a separate business bank account for an LLC is crucial for several reasons, especially the legal and financial protection it provides.
Why it’s best to keep your finances separate: When an LLC operates through a dedicated business bank account, it enhances the company’s credibility by establishing a clear division between personal and business finances. This separation is essential for maintaining the limited liability status that protects personal assets from business debts and liabilities.
Also, a business bank account simplifies accounting and tax preparation by consolidating all business transactions in one place, making it easier to track expenses, manage cash flow, and prepare financial statements.
Banking options to consider: When selecting a business bank account for an LLC, it’s important to consider features that align with your company’s needs, such as low fees, easy online banking access, integration with accounting software, and robust customer support. Options like Found, Relay, and Mercury offer a range of services tailored to small businesses and startups. Each option caters to different aspects of business banking needs for small businesses.
Obtain a Certificate of Good Standing
In Utah, while there isn’t a conventional Certificate of Good Standing, various entities provide documents serving a similar function. For businesses, the Certificate of Existence fulfills this role. Issued by the Utah Department of Commerce, this confirms a business entity’s registration and good standing within the state.
This certificate can be acquired through online, mail, or in-person methods for $15, plus a $3.90 fee if mailed.
Build a website
Starting a website for your LLC immediately is a strategic move to establish an online presence and reach a wider audience. While every LLC owner knows a website is necessary, you might not know where to start. Follow these steps to get started:
- Search for and purchase a domain name.
- Sign up for web hosting.
- Pick a web builder like Domain.com or GoDaddy to create a site with no coding experience necessary.
- Tailor your site to your customers, adding appropriate pages, content, and images.
- If you’re selling goods, add an e-commerce section to your site.
- Review, test, and publish your site.
Utilizing website builders: Utilizing platforms like Domain.com and GoDaddy can significantly streamline the process, and both offer comprehensive services for obtaining domain names and building websites. Both are particularly user-friendly, making it easy for entrepreneurs to find and purchase the perfect domain name that aligns with their business identity.
Once the domain is secured, intuitive site-building tools and templates allow for creating a professional-looking website without the need for extensive technical knowledge.
Costs to set up an LLC in Utah
| Expense | Cost |
|---|---|
| State filing fee (Articles of Organization) | $59 |
| Registered agent service (optional) | $0-$300/year |
| Operating agreement | Free (self-prepared) |
| EIN from IRS | Free |
| Business licenses/permits | Varies by city/county |
| Annual report fee | $18 |
| Estimated total startup cost | $59-$359 |
Average cost to set up an LLC in Utah: $79-$279
If you’re ready to set up an LLC in Utah, know your initial start-up fees. Here are the three biggest costs to be aware of:
- Incorporation fees: The primary cost of LLC formation lies in the Utah Certificate of Organization filing fee, which amounts to $59.
- Annual Report filing fees: For ongoing compliance, LLCs must file annual reports for $20 per year to maintain good standing with the state. This form is filed with the secretary of state and is similar to your formation documents.
- Registered agent services fees: While professional services are optional, many LLC owners opt for assistance to ensure a smooth start for their businesses like a registered agent service. By hiring a commercial service to serve as your company’s point of contact, you ensure all official documents are securely and confidentially received.
Foreign LLC registration
An LLC formed in a state other than Utah that intends to do business in the state must register with the Utah Division of Corporations.
Complete these steps to do business in Utah as a foreign LLC:
- Comply with Utah LLC naming restrictions and confirm that the LLC’s name is available using the Utah Division of Corporations Business Search.
- Appoint a Utah registered agent.
- File a Foreign Registration Statement with the Utah Division of Corporations online or by postal mail. The filing fee is $59. The application must be accompanied by either a Certificate of Good Standing or a Certificate of Existence from the LLC’s home state that is dated fewer than 90 days prior to its filing with the Ohio Secretary of State.
FAQs
What is the process for registering an LLC in Utah?
The process of forming an LLC in Utah involves several steps, including choosing a unique name for your business, filing the Utah Certificate of Organization, appointing a registered agent, and drafting an operating agreement if desired. Once these requirements are fulfilled and the necessary fees are paid, your LLC will be officially registered with the state.
Do I need to have a physical address in Utah to form an LLC?
Yes, you’ll need to obtain a physical address for your Utah LLC’s registered agent, which cannot be a P.O. Box. However, you can use a P.O. Box as your business address for mailing purposes if desired.
Are there any restrictions on the types of businesses that can form an LLC in Utah?
In Utah, there are generally no restrictions on the types of businesses that can form an LLC, including sole proprietorships looking to transition to a more formal business structure. LLCs offer liability protection and other benefits that can be advantageous for sole proprietors seeking to separate their personal and business affairs.
What is the process for dissolving an LLC in Utah?
To dissolve an LLC in Utah, you must file Articles of Dissolution with the Utah Division of Corporations and Commercial Code. This document formally terminates the existence of your LLC and should be accompanied by any required fees and paperwork. Once approved, your Utah LLC will no longer be considered active, and you’ll need to fulfill any remaining obligations before officially closing the business.
Can I trademark my LLC's name in Utah?
Yes, you can trademark your LLC’s name in Utah to protect its identity and brand. To trademark your LLC’s name in Utah, you would need to file a trademark application with the Utah Department of Commerce, Division of Corporations and Commercial Code, or seek federal trademark registration through the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO).